昨天我們讓 /search API 成形,雖然只是回假資料,但已經建立了 API 雛型。
今天要讓服務更可靠:加入 context/timeout。
這一步很重要,因為:
/search 會呼叫下游(Elasticsearch、DB、甚至外部 API)。舉例:
504 Gateway Timeout(或自定義錯誤),請求不會無限佔住資源。/search Handler修改 main.go 裡的 searchHandler,加入 context with timeout。
我們模擬「下游呼叫」用 time.Sleep,但會被 context 控制。
// 1) 從當前請求的 context 衍生一個有時限的 ctx
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(r.Context(), 2*time.Second)
defer cancel()
// 3) 監聽 ctx,時間到(或客戶端中斷)就走這裡
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
http.Error(w, "search timeout", http.StatusGatewayTimeout)
return
// ...
}
// 2) 開 goroutine 模擬「呼叫下游」需要時間
resultCh := make(chan SearchResponse, 1)
go func() {
// 假裝下游很慢:睡 3 秒(故意比 2 秒 timeout 還長)
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)
resultCh <- SearchResponse{
Query: query,
Hits: []SearchResult{
{ID: 1, Title: "Learning Go"},
{ID: 2, Title: "Go Concurrency Patterns"},
},
}
}()
select {
case <-ctx.Done(): // ←(A)context 超時/取消
http.Error(w, "search timeout", http.StatusGatewayTimeout)
return
case resp := <-resultCh: // ←(B)下游結果回來
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
_ = json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(resp)
}
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"time"
)
// 假資料
type SearchResult struct {
ID int `json:"id"`
Title string `json:"title"`
}
type SearchResponse struct {
Query string `json:"query"`
Hits []SearchResult `json:"hits"`
}
func searchHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
query := r.URL.Query().Get("q")
if query == "" {
http.Error(w, "missing query parameter: q", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// 建立帶有 timeout 的 context
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(r.Context(), 2*time.Second)
defer cancel()
// 模擬下游呼叫(例如 Elasticsearch)
resultCh := make(chan SearchResponse, 1)
go func() {
// 假裝需要 3 秒(比 timeout 長)
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)
resultCh <- SearchResponse{
Query: query,
Hits: []SearchResult{
{ID: 1, Title: "Learning Go"},
{ID: 2, Title: "Go Concurrency Patterns"},
},
}
}()
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
// timeout 或被取消
http.Error(w, "search timeout", http.StatusGatewayTimeout)
return
case resp := <-resultCh:
// 正常拿到結果
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
if err := json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(resp); err != nil {
http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("encode error: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
}
}
func healthHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintln(w, "ok")
}
func main() {
cfg := LoadConfig()
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/healthz", healthHandler)
mux.HandleFunc("/search", searchHandler)
handler := LoggingMiddleware(RecoveryMiddleware(mux))
log.Printf("Server listening on %s", cfg.Port)
if err := http.ListenAndServe(cfg.Port, handler); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
新增 search_timeout_test.go:
package main
import (
"context"
"net/http"
"net/http/httptest"
"testing"
"time"
)
// 目前的實作:handler 會在 2s 超時、下游模擬 3s -> 必定 504
func TestSearchHandler_ServerTimeout(t *testing.T) {
t.Parallel()
req := httptest.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, "/search?q=golang", nil)
rr := httptest.NewRecorder()
// 直接呼叫目前的 handler
searchHandler(rr, req)
if rr.Code != http.StatusGatewayTimeout {
t.Fatalf("status got %d, want %d", rr.Code, http.StatusGatewayTimeout)
}
want := "search timeout\n"
if rr.Body.String() != want {
t.Fatalf("body got %q, want %q", rr.Body.String(), want)
}
}
// 客戶端主動取消(早於 2s timeout),也應拿到 504
func TestSearchHandler_ClientCancel(t *testing.T) {
t.Parallel()
// 建立一個會在 200ms 取消的 context,包在 request 裡
parent := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(parent, 200*time.Millisecond)
defer cancel()
req := httptest.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, "/search?q=golang", nil).WithContext(ctx)
rr := httptest.NewRecorder()
searchHandler(rr, req)
if rr.Code != http.StatusGatewayTimeout {
t.Fatalf("status got %d, want %d", rr.Code, http.StatusGatewayTimeout)
}
}
// 缺少 q 參數 -> 400
func TestSearchHandler_BadRequest(t *testing.T) {
t.Parallel()
req := httptest.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, "/search", nil)
rr := httptest.NewRecorder()
searchHandler(rr, req)
if rr.Code != http.StatusBadRequest {
t.Fatalf("status got %d, want %d", rr.Code, http.StatusBadRequest)
}
}
main()main() 引用了其他檔案的 function,所以執行測試時需要包含所有相關的 .go 檔案才能通過編譯。go test -v main.go middleware.go config.go search_timeout_test.go
預期結果:
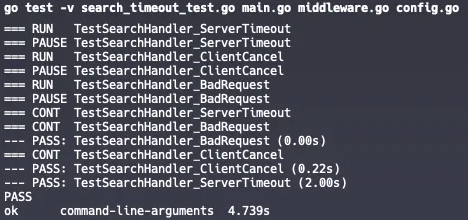
今天我們完成了:
context.WithTimeout 為 /search 加上 timeout這讓服務更健壯,未來即使 Elasticsearch 出現延遲或故障,也不會拖垮整個 Go 服務。
👉 明天(Day 7),我們要進一步優化 錯誤策略:用 %w 包裝錯誤,並根據錯誤類型做分類重試(退避 + 抖動)。
